What is a Machine for Spinning Wool and How Does It Work?
The "machine for spinning wool" is a fascinating innovation that has transformed textile manufacturing. In recent years, the wool spinning industry has seen significant growth. According to the Wool and Fiber Industry Report 2022, the global demand for spun wool products is expected to rise by 5% annually. This increase is driven by a resurgence in natural fibers, aligning with consumer preferences for sustainability.
Expert in textile technology, Dr. Emily Turner, highlights the importance of these machines. She states, “The efficiency and precision of the machine for spinning wool have redefined quality standards in wool production.” These machines make it possible to convert raw wool into high-quality yarns consistently. However, despite advancements, challenges remain. Many facilities still rely on outdated spinning technologies, which can lead to inefficiencies.
The process itself may seem straightforward, yet its complexities can lead to significant variances in quality. Spinning wool requires careful handling and precise techniques to achieve desired results. As the industry evolves, the role of machines becomes even more critical. Recognizing these nuances is essential for manufacturers to stay competitive in this rapidly changing market.
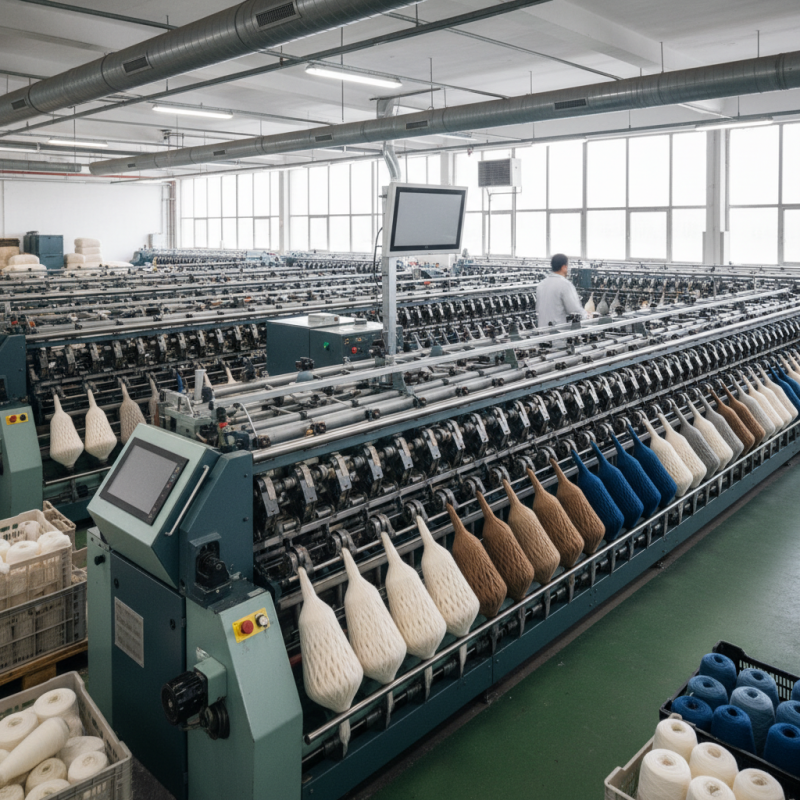

What is a Wool Spinning Machine? Definition and Overview
A wool spinning machine is a vital tool in the textile industry. It transforms raw wool into yarn through a multi-step process. The machine carded wool fibers are aligned and twisted, creating a continuous strand suitable for knitting or weaving. Reports indicate that the global market for spun yarn reached approximately $300 billion in 2021, underlining the significance of efficient spinning technology.
For those exploring wool spinning, consider the machine's efficiency. Modern machines can produce up to 50 kg of yarn per hour. In contrast, manual methods yield significantly less. However, the investment in technology can be daunting for small businesses. It's essential to weigh costs against potential output.
Tips: Prioritize maintenance. Regularly check the machine to prevent downtimes. Understand your wool type. Different fibers require different settings. This knowledge can optimize production. Reflection on this can lead to improved processes and gains. Each minor adjustment can enhance the final product's quality.
What is a Wool Spinning Machine? Definition and Overview
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | To spin raw wool fibers into yarn. |
| Types | Hand-spinning and machine-spinning, including modern automated models. |
| Components | Spindle, bobbin, wheel, drive band (in traditional models). |
| Process | Fibers are fed into the machine, twisted, and wound onto a bobbin. |
| Materials | Primarily wool, but can include blends with other fibers. |
| Automation | Modern machines can automate tension, speed, and bobbin change. |
| Applications | Used in textile manufacturing for producing yarns for knitting and weaving. |
Historical Development of Wool Spinning Machines and Their Impact
The history of wool spinning machines is fascinating. Early spinning methods relied on manual tools. The spinning wheel, invented in the Middle Ages, sped up the process. It allowed artisans to spin fibers into yarn more efficiently. Nonetheless, it had its limitations. The reliance on human power meant production was slow and inconsistent.
The Industrial Revolution marked a turning point. Innovations like the spinning jenny transformed wool production. This machine could spin multiple spools at once. It drastically increased output and reduced labor costs. However, many skilled workers lost their jobs. This created tension in the workforce. The shift from home-based production to factories was not without struggle. Some workers resisted, fearing for their craft.
Wool spinning machines today are advanced, incorporating technology that ensures quality. But, even with improvements, challenges remain. Environmental concerns arise regarding waste and sustainability. Changing consumer demand also impacts wool production. Reflecting on the past helps us navigate current and future challenges in the industry. What lessons can we learn from history?
Types of Wool Spinning Machines: Spindle, Flyer, and Ring Spinning
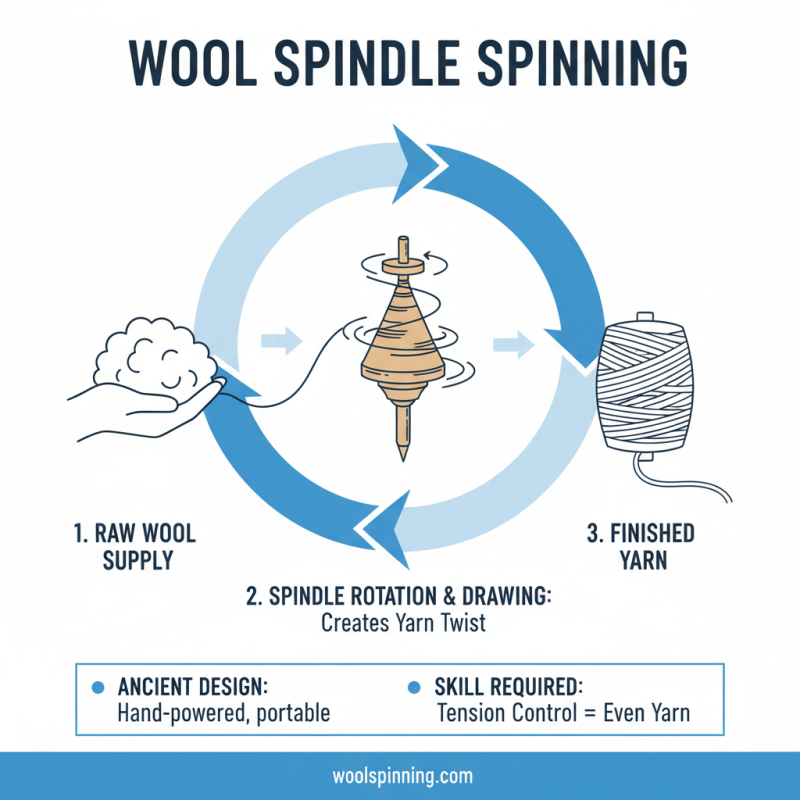
Wool spinning machines come in various types, each with its unique features. The spindle spinning machine is one of the oldest designs. A spindle rotates as wool is drawn out. This creates a thin strand of yarn. The process requires skill. Operators must manage tension carefully. A mistake can lead to uneven yarn.
Flyer spinning machines work differently. They use a flyer that helps twist the fibers. This method produces a more consistent yarn. However, it can be complex to operate. Operators need to monitor the spinning speed closely. It’s easy to lose focus and create flaws.
Ring spinning machines are widely used today. They combine efficiency with quality. The ring system pulls the fibers together, creating strong yarn. Despite their popularity, they require regular maintenance. Neglecting upkeep can result in machine failure. Each type of spinning machine has its merits and challenges. The craft of spinning remains an art, blending technology with skill.
Mechanics of Wool Spinning: How Fiber is Transformed into Yarn
The process of transforming wool fibers into yarn is a fascinating blend of art and science. Wool fibers are typically harvested from sheep, which can vary significantly in quality. According to the International Wool Textile Organisation, in 2022, the global wool production reached approximately 1.1 million tonnes. This vast amount reflects the industry's scale and the intricate transformations that follow.
Wool spinning begins with cleaning the raw fleece. This step removes grease, dirt, and other impurities. After cleaning, the fibers are carded. During carding, individual wool fibers are separated and aligned into a continuous web. This process is crucial as it ensures even spinning. Reports indicate that carding can improve production efficiency by up to 15%.
Once carded, the fibers are spun into yarn using a spinning machine. The spinning process involves twisting the carded fibers to create a cohesive thread. The tension applied during spinning affects the yarn’s strength and texture. A study from the Woolmark Company highlights that careful management of spinning tension can increase yarn durability by 30%. However, inaccuracies in fiber alignment can lead to weak spots. This underscores the need for precision throughout the spinning process.
Industry Statistics: Global Wool Production and Spinning Technology Trends
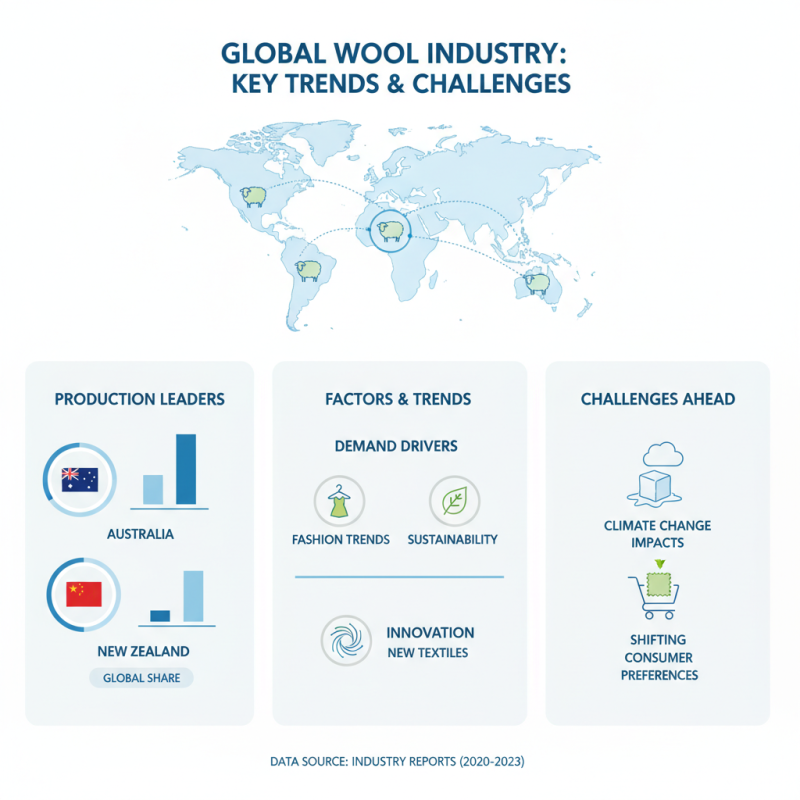
Wool production is a significant global industry. In recent years, the demand for wool has fluctuated. Factors such as fashion trends and sustainability movements have impacted production rates. Different countries contribute to overall production, each with unique methods. Australia remains a leader, followed closely by China and New Zealand. Despite this, we face challenges. Climate change and shifting consumer preferences test the resilience of this industry.
Spinning technology has advanced, reflecting these trends. Traditional hand spinning is now complemented by modern machines. These machines increase efficiency and consistency, producing high-quality yarn. Yet, this shift raises questions. Are we sacrificing artisan skills for mass production? The balance between technology and craftsmanship requires reflection. Innovations, such as automated spinners, can reduce labor but may overlook the art of spinning. Acknowledging this tension is essential for the industry’s future. As we move forward, we must consider the value of both tradition and technology in wool production.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Best Machine for Spinning Wool Based on Expert Data and User Reviews
-

Top 10 Wool Spinning Machines You Need to Know for Your Crafting Projects
-

Why You Should Choose a Home Wool Spinning Machine for Your Crafting Needs
-

Why You Should Choose an Automatic Wool Spinning Machine for Your Business
-

2025 Top 10 Yarn Manufacturing Machines: Boost Efficiency with Advanced Technology
-

Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Right PP Multifilament Yarn Machine
